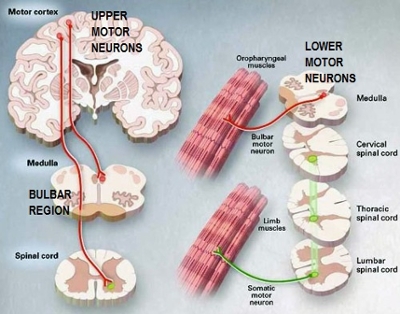
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is also known as Motor Neuron Disease, Lou Gehrig's Disease, and Charcot's Disease (in Europe). ALS is a disease of "motor neurons", the cells that initiate and control the movement of muscles. Motor neurons are characterized as "upper" if they originate in the brain, and "lower" if they originate in the spinal cord. ALS affects both upper and lower motor neurons, although each person with ALS has varying amounts of upper and lower motor neuron disease. Upper motor neuron disease causes stiffness, which is called "spasticity". Lower motor neuron disease causes weakness, loss of muscle ("atrophy") and muscle twitching ("fasciculations"). ALS may begin with abnormalities of upper or lower motor neurons. "Bulbar" ALS, also called Progressive Bulbar Palsy, prominently affects the muscles involved in speech, swallowing, and tongue movements.
Primary Lateral Sclerosis (PLS) is a variant of ALS that affects only upper motor neurons. People with PLS have problems with severe stiffness ("spasticity") that may affect their ability to speak, swallow, and walk.
Progressive Muscular Atrophy (PMA) affects only lower motor neurons, causing weakness and loss of muscle bulk ("atrophy").
PLS and PMA are considered variants of ALS, and people with these disorders may progress to develop true ALS.

