Ultrasound-guided HDR Prostate Brachytherapy
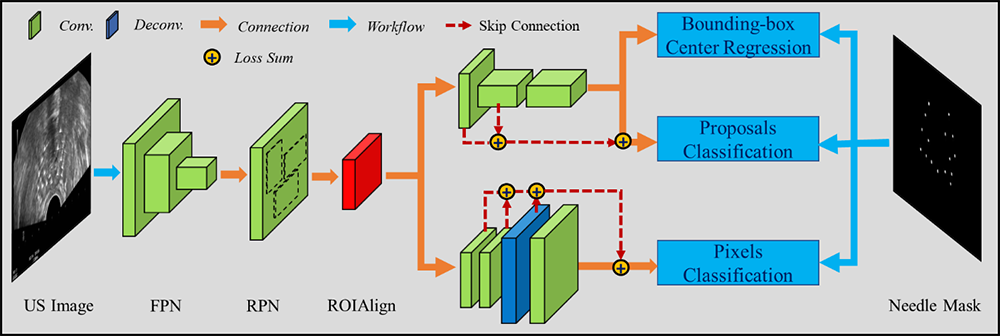
Related publications:
Zhang Y, He X, Lei Y, Wang T, Mao H, Jani A, Patel P, Curran W, Liu T and Yang X*. “Multi-needle Detection in 3D Ultrasound Images Using Unsupervised Order-graph Regularized Sparse Dictionary Learning,” IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 39(7):2302-2315, 2020.
Lei Y, Tian S, He X, Wang T, Wang B, Pretesh P, Jani A, Mao H, Curran W, Liu T and Yang X*. “Ultrasound Prostate Segmentation Based on Multi-Directional Deeply Supervised V-Net," Medical Physics, 46(6):3194-3206, 2019.
Zhang Y, Lei Y, Qiu R, Wang T, Wang H, Jani A, Curran W, Patel P, Liu T and Yang X*. “Multi-needle Localization with Total Variation Regularized Deep Supervised Attention U-Net in Ultrasound-guided HDR Prostate Brachytherapy," Medical Physics, 47(7):2735-2745, 2020.
Zeng Q, Fu Y, Tian Z, Lei Y, Zhang Y, Wang T, Wang H, Mao H, Liu T, Curran W, Jani A, Patel P and Yang X*. “Label-Driven MRI-US Registration Using Weakly-Supervised Learning for MRI-guided Prostate Radiotherapy," Physics in Medicine and Biology, 65(13):135002, 2020.
Fu Y, Lei Y, Wang T, Patel P, Jani A, Mao H, Curran W, Liu T and Yang X*. "Biomechanically Constrained Non-rigid MR-TRUS Prostate Registration using Deep Learning based 3D Point Cloud Matching," Medical Image Analysis, 67,101845, 2021.
Deep Ultrasound Imaging
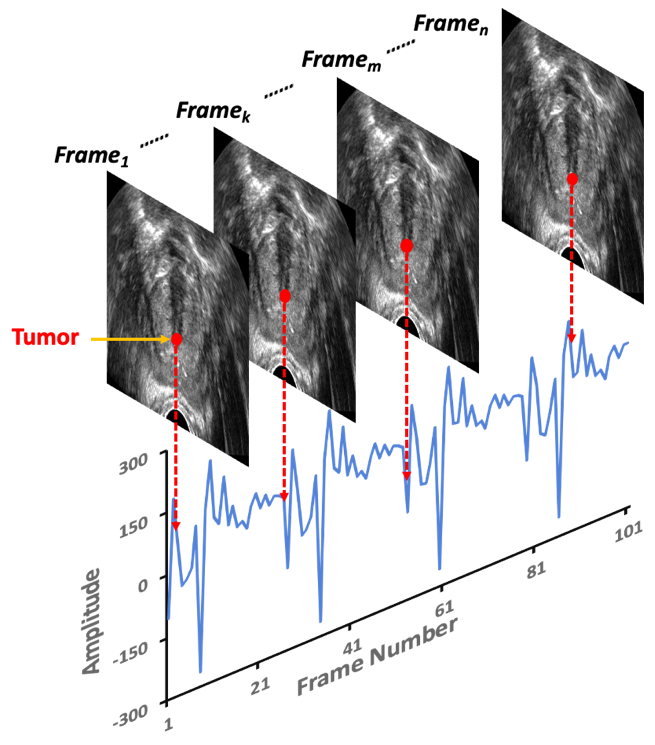
Using deep learning techniques to analyze ultrasound (US) data over a sequence of US frames and explicitly model the temporal information in US sequences is a new paradigm for tissue characterization. The deep US-guided tumor tracking system will improve the outcomes and reduce the normal tissue toxicity of cancer radiotherapy.
Related publications:
Lei Y, Momin S, Roper J, Patel P, Curran WJ, Liu T and Yang X*. “Motion tracking in 3D ultrasound imaging based on Markov-like deep-learning-based deformable registration.” Proc. of SPIE, 11602:1160215, 2021.
Quantitative Ultrasound Imaging for Radiation Toxicity Evaluation
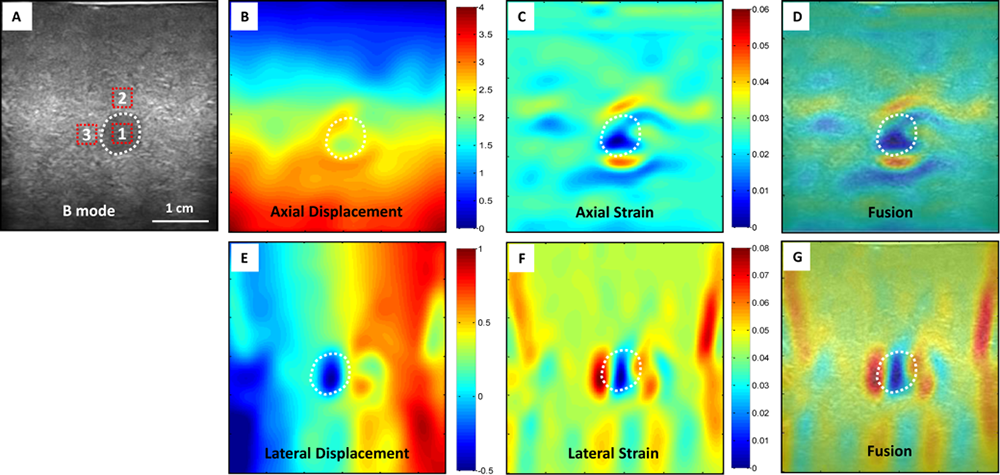
Related publications:
Zhou B, Yang X, Curran W and Liu T. "Artificial Intelligence in Quantitative Ultrasound Imaging: A Review,” Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine, 2021 (In press)
Yang X*, Torres M, Kirkpatrick S, Curran W and Liu T*. "2D Strain Measurement for Lymphedema Tissue Using Deformable Registration of Ultrasound Images: A Feasibility Study.” Plos One, 12(8): e0181250, 2017.
Yang X, Yoshida E, Cassidy R, Beitler J, Yu D, Curran W and Liu T. “Quantitative Ultrasonic Nakagami Imaging of Neck Fibrosis After Head and Neck Radiation Therapy.” International Journal of Radiation Oncology • Biology • Physics (IJROBP), 92(2), 407-414, 2015.
Yang X, Tridandapani S, Beitler J, Yu D, Wu N, Bruner D, Curran W and Liu T. “Ultrasonic Nakagami-Parameter Characterization of Parotid-Gland Injury Following Head-and-Neck Radiotherapy.” Medical Physics, 41(2), 022903, 2014.
Yang X, Beitler J, Tridandapani S, Yu D, Cheng Z, Bruner D, Curran W and Liu T. “Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonic Histogram Features to Evaluate Radiation Toxicity of the Parotid Glands: A Clinical Study of Xerostomia Following Head-and-Neck Cancer Radiotherapy.” Academic Radiology, 21(10), 1304-13, 2014.
Learning-Based Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging
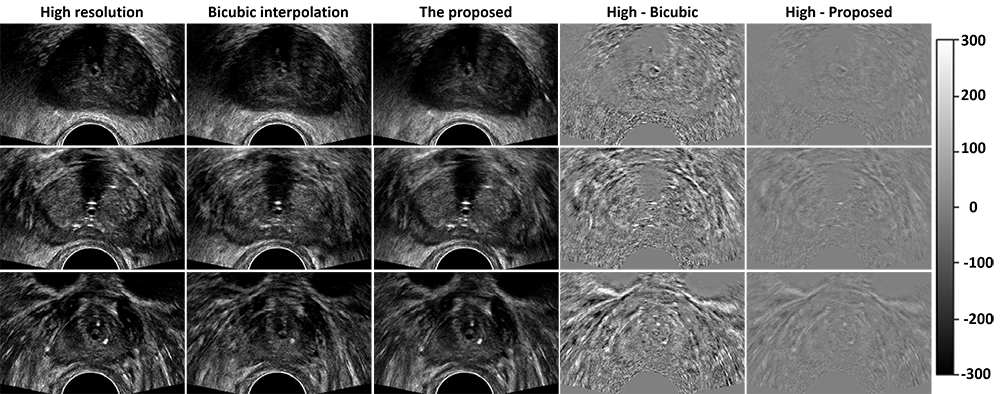
A routine 3D transrectal ultrasound volume is usually captured with large slice thickness (e.g. 2-5mm). Such ultrasound images with low out-of-slice resolution affect contouring and needle/seed detection in prostate brachytherapy. The purpose of this study is to develop a deep-learning-based method to construct super-resolution images from routinely captured prostate ultrasound images for brachytherapy.
Related publications:
Dai X, Lei Y, Wang T, Axente M, Xu D, Patel P, Jani A, Curran WJ, Liu T, Yang X*. “Self-supervised Learning for Accelerated 3D High-resolution Ultrasound Imaging.” Medical Physics, 48(7):3916-3926, 2021.
High-Resolution Ultrasound for Skin Imaging
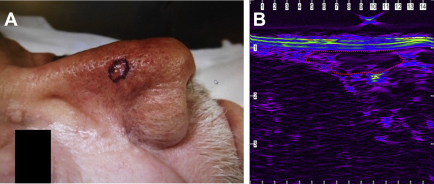
Skin cancer is the most common type of malignancy, and radiation therapy is an excellent alternative treatment for patients who are medically inoperable or refuse surgery. High-dose-rate (HDR) surface brachytherapy can spare adjacent and deeper normal tissue from radiation doses while delivering a larger radiation dose to skin cancers. Therefore, surface brachytherapy is especially suitable for patients who have lesions that are located in sensitive anatomic regions such as the scalp, eyes, or nose. Ultrasound guidance is needed typically for tumor localization during brachytherapy for prostate and cervical cancers, but its use for skin cancer treatment is uncommon. 3D high-resolution ultrasound guidance is used during iridium-based brachytherapy for skin cancer.
Related publications:
Zhu S, Yang X*, Xu K, Jeong J and Khan M*(*Co-corresponding authors). "High-resolution ultrasound-guided high-dose-rate (HDR) surface brachytherapy for basal cell carcinoma of the skin: a case report", Advances in Radiation Oncology, 3(4), 591–594. 2018.

