These cases focus on commonly encountered pitfalls in obtaining the upper quadrant views for the FAST exam.
Take a look at this right upper quadrant view.
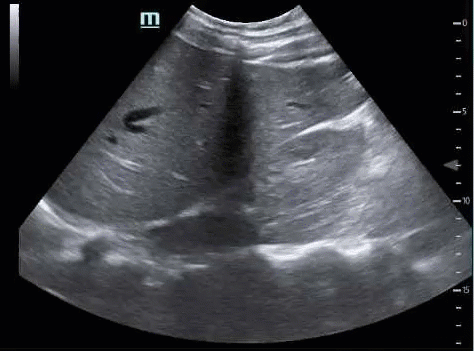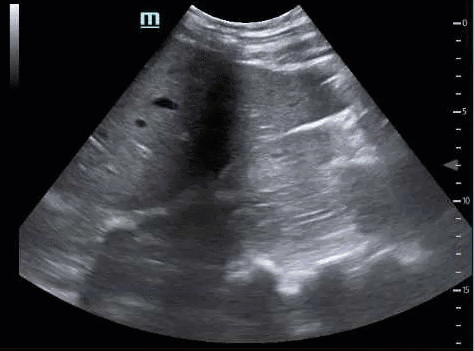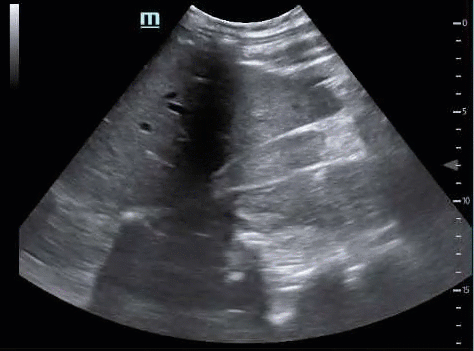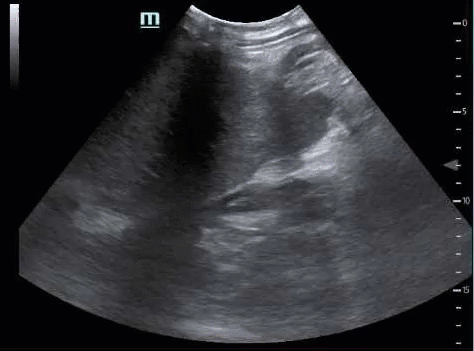
If you do not visualize the inferior edge of the liver, you will miss free fluid. If the kidney does not disappear in both directions, you have not fully interrogated the hepatorenal interface, and you will miss free fluid.
Tips for the left upper quadrant
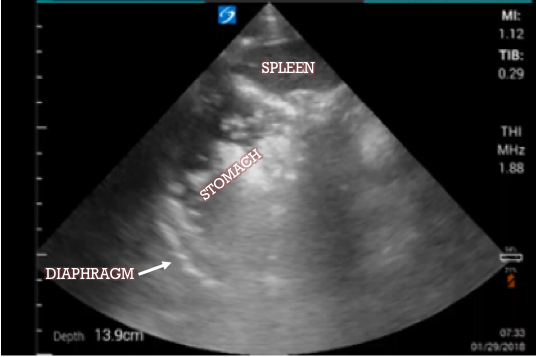
What do you make of this view of the left upper quadrant?
- Nothing, the probe is too cephalad for an accurate assessment
- Nothing, the probe is too anterior for an accurate assessment
- The patient is s/p splenectomy
- The spleen is shattered
The structure seen next to the partially visualized spleen is a full stomach. It is well-circumscribed, and all that echogenic debris within it is undigested food. This commonly happens when the probe is directed too anterior (b). If you see the stomach, slide the probe back towards the bed. Often, you will need to have your knuckles flat against the bed for an adequate view. A large stomach can not only get in the way of your FAST but it may have implications for paralyzing for intubation. You should at minimum have good suction (but often double) set up.
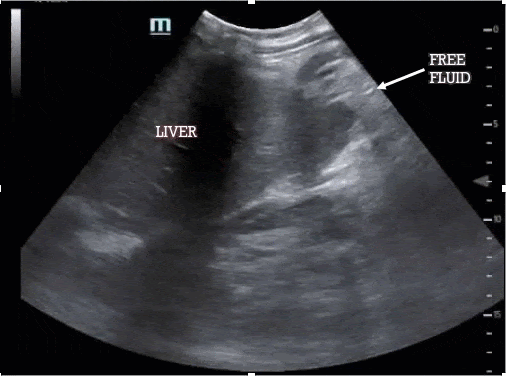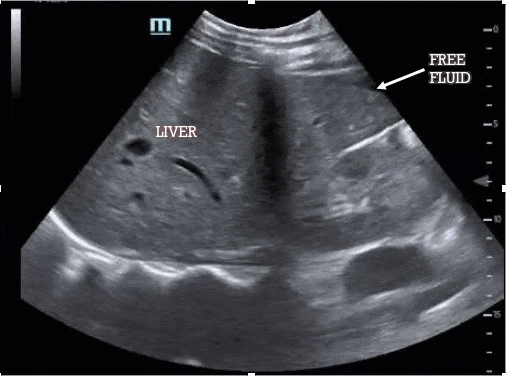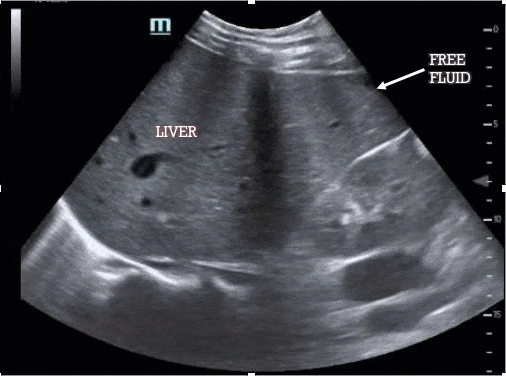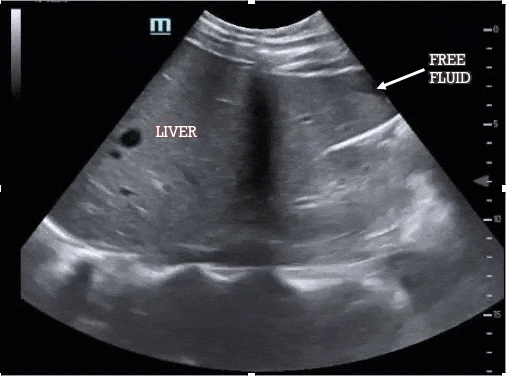
The most sensitive location for left upper quadrant free fluid is the subdiaphragmatic space (not the splenorenal interface, which should also be visualized) and so your FAST is considered incomplete if you do not capture the diaphragm. As before, the spleen/kidney should disappear in both directions as you move the probe.
One final point. The location of free fluid does not necessarily correlate with the origin of bleeding. We have examples from the Emory archives of renal fracture with most fluid collecting on the contralateral side, ruptured ectopic pregnancy with most of the fluid around the spleen, etc.
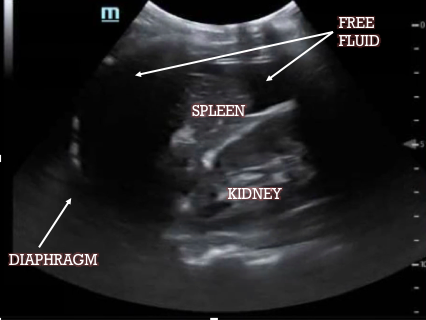

The location of free fluid does not necessarily correlate with the origin of bleeding. We have examples from the Emory archives of renal fracture with most fluid collecting on the contralateral side, ruptured ectopic pregnancy with most of the fluid around the spleen etc.

