Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) is a research initiative created by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), seeking to understand, prevent, and treat Long COVID. RECOVER is an observational study with cohorts of participants whom are engaging with the study for several years.
Emory University and it's local partners are leading the Atlanta HUB for a nationwide study to identify why some people have prolonged symptoms (long COVID) or develop new or returning symptoms after an acute COVID infection.

The RECOVER initiative has adult and pediatric participants throughout the United States and territories. RECOVER Atlanta is one of 14 adult consortiums.
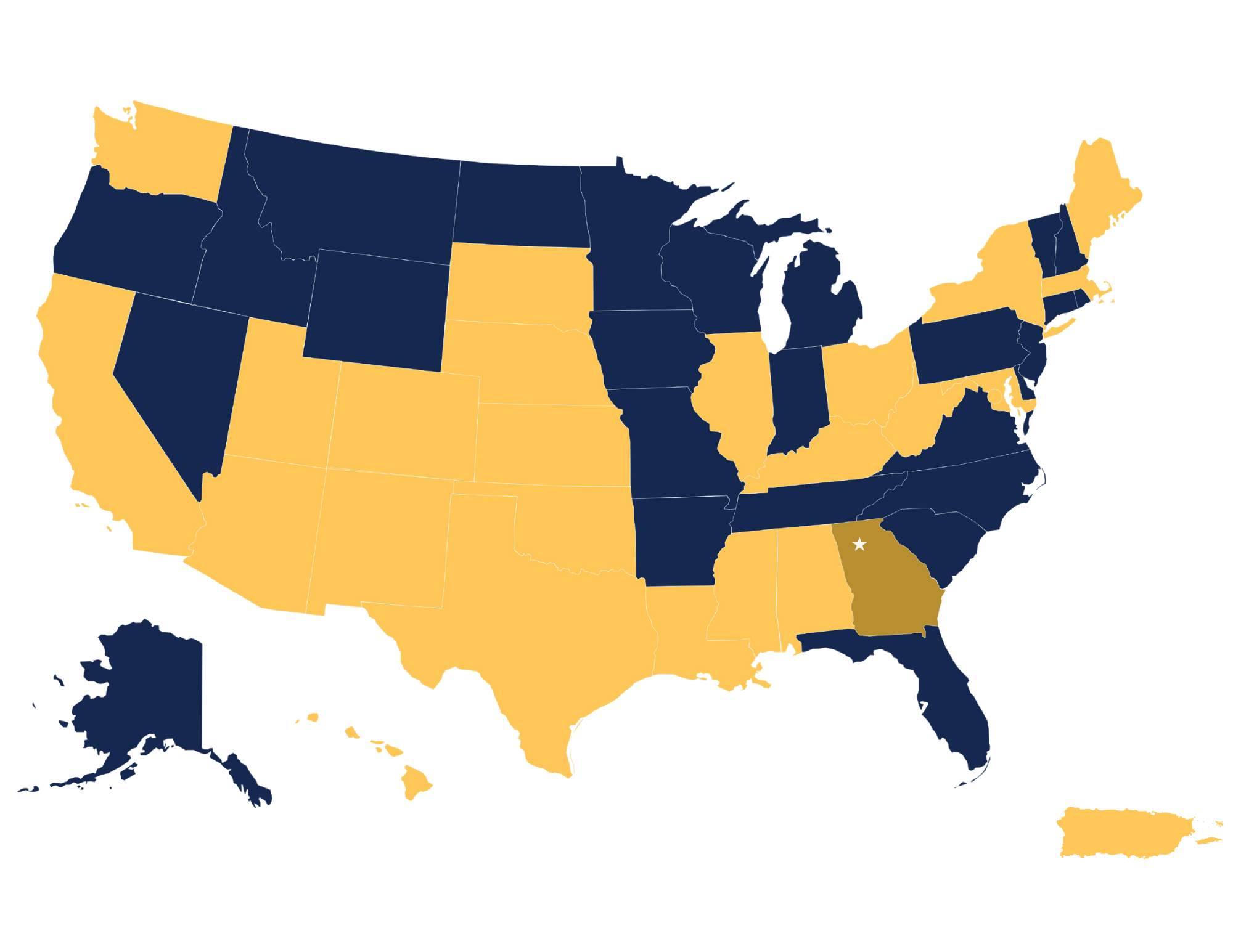
The participant population of RECOVER Atlanta represent the following:

SARS-CoV-2 is a virus that can infect the body, causing Coronavirus disease (COVID). Recovery from COVID can vary from person to person.
For some people, symptoms of COVID can last weeks or months after the acute infection has passed.
For other people, new symptoms may appear after the acute infection has passed whether they had symptoms during the acute infection or not.
There are more than 200 symptoms of Long COVID.
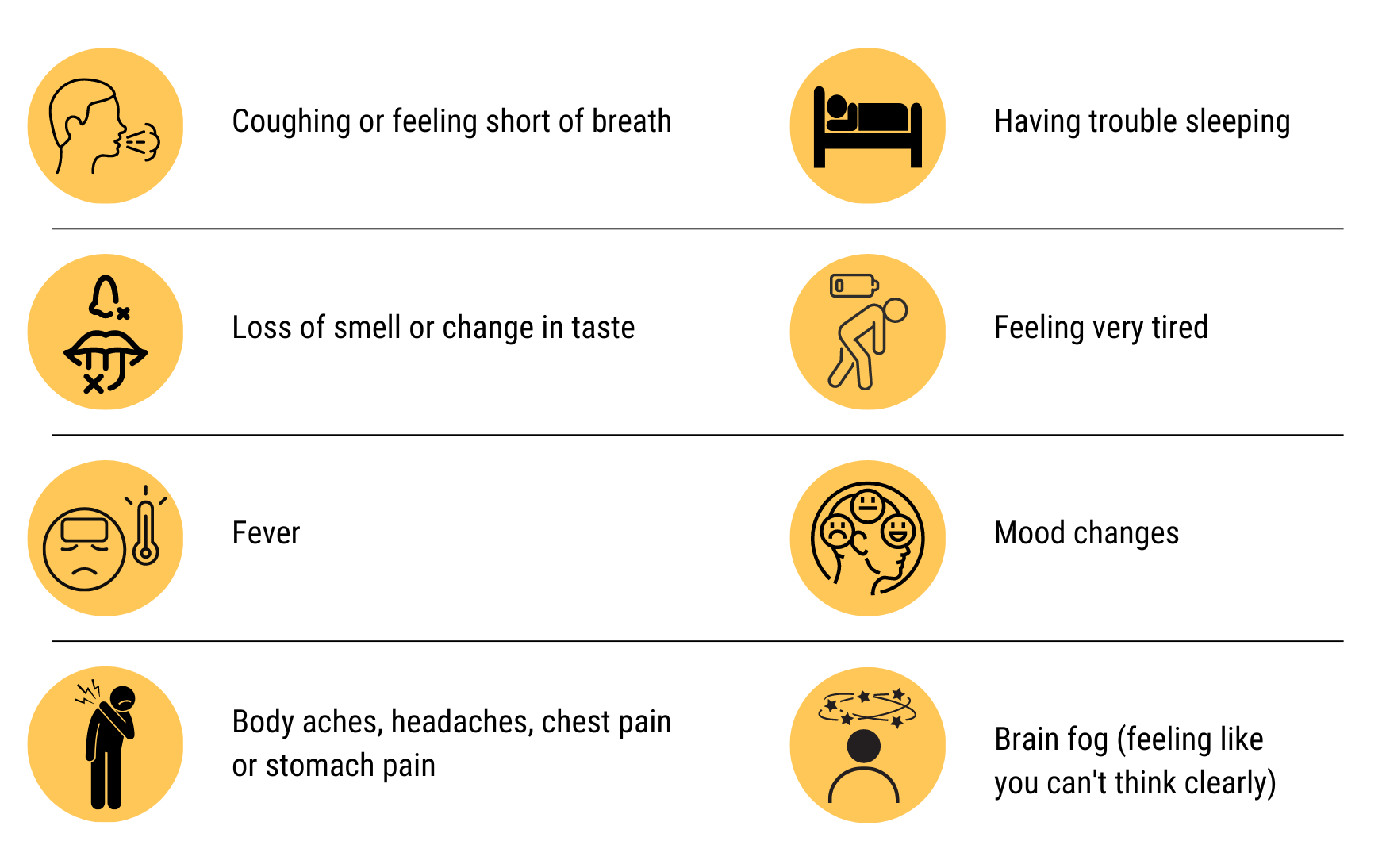
Together, these and other health effects of the virus are called post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC) infection, or Long COVID. Long COVID refers to what happens after (post) the acute infection with the virus and is relevant whether a person has been diagnosed with COVID or not. Even if someone did not experience symptoms, Long COVID is still relevant because there could be effects after acute infection.
Long COVID is characterized 30 days after acute infection.


