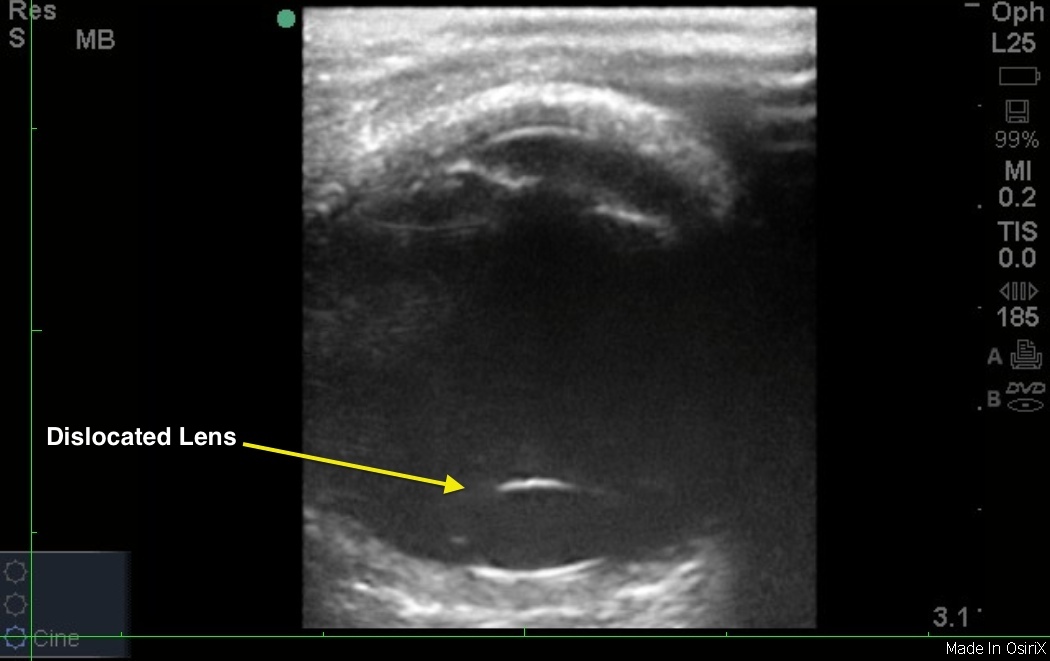
The linear probe is best for imaging the eyeball, as it provides rich detail of superficial structures. Before you ultrasound, the eye, place a clear dressing (e.g., Tegaderm) over the eye. Placing plenty of gel over the dressing allows you to image without putting pressure on the eye. The lens apparatus is typically seen suspended within the anterior eye with the anechoic fluid vitreous body filling the posterior chamber. However, in their patient with lens dislocation, Drs. Little and Wolf see the lens floating in the posterior chamber.
Image 1: Lens Dislocation
Clinical Importance
Emergency bedside ultrasound is highly accurate for ruling out and diagnosing ocular pathology in patients presenting to the emergency department. Further, it can help to differentiate between pathology that needs immediate ophthalmologic consultation and that which can be followed up on an outpatient basis. As a fluid-filled structure, the eye is easy to visualize with ultrasound. The possibility of elevated intraocular pressure due to lens dislocation or other types of secondary glaucoma should be considered after blunt ocular trauma. Also, remember if there is any suspicion of the ruptured globe, avoid the ocular ultrasound, as any pressure can cause extrusion of irreplaceable vitreous out of the eye.
Image credit: Drs. Little and Wolf

