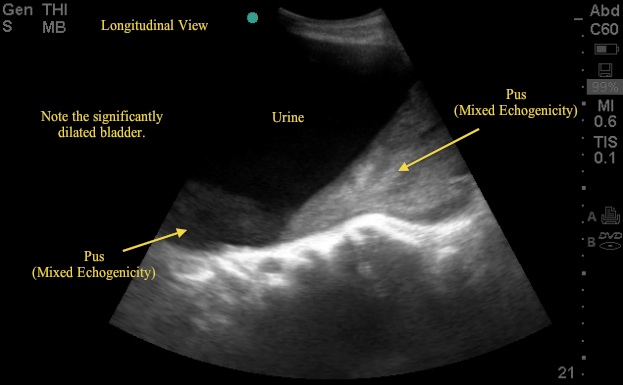
This week's Image of the Week is from an evaluation of an 83 yo M with abdominal distention and urinary sediment, a bedside US captured the following bladder images (Images 1, 2, and 3). These images show a significant abnormality in the bladder and kidney requiring prompt consultation and management.
Image 1
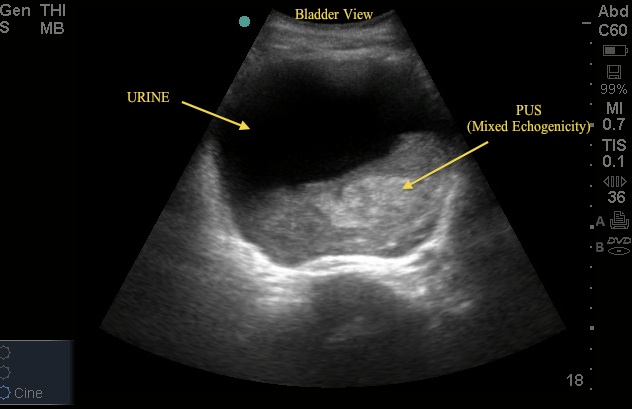
Image 2
Probe placement for bladder imaging is shown in images 4 (transverse) and 5 (sagittal). Using the curvilinear probe, the transverse view is obtained with the probe indicator to the right of the patient. The sagittal view is obtained by rotating the probe 90 degrees - the indicator now toward the head of the patient. From both positions, subtle fanning movements permits full visualization of the fluid-filled bladder.
Image 3
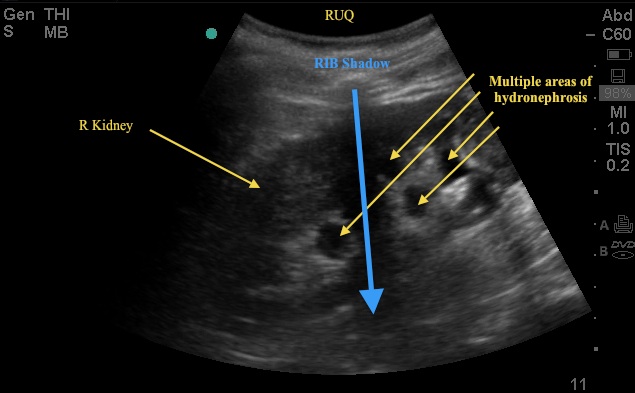
Image 4
Image 5
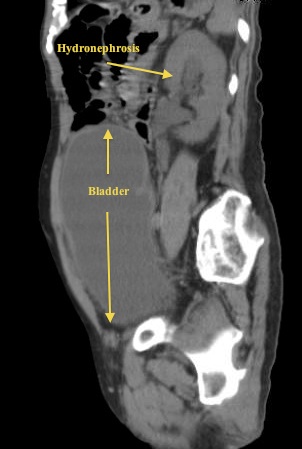
Looking back at US images 1, 2 and 3, the critical finding is a grossly distended bladder with a large clot of mixed echogenicity – in this case representing pus in the bladder. The patient has a history of BPH with outflow obstruction and uses a chronic Foley catheter. He was sent to the ER with concern for infection given pus/sediment in the Foley bag. On labs, the patient had an acute elevation of his Cr and a WBC >20. The patient arrived tachy but afebrile. See the attached sagittal CT image (6) showing both the enlarged bladder and associated hydronephrosis – both of which were noted on the bedside US.
Image 6
2012

